By Dr Eloi de Clermont-Tonnerre and Pr Barbara Hersant
For many years now, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections have often been used for aesthetic purposes to treat wrinkles, particularly in women. However, the demands from men are constantly increasing. Since the morphology of the male face, as well as men’s wishes, are different from women’s, we must respect certain particularities when injecting botulinum toxin. This recap goes through the specific features of injecting botulinum toxin in men.
 Glabellar
Glabellar
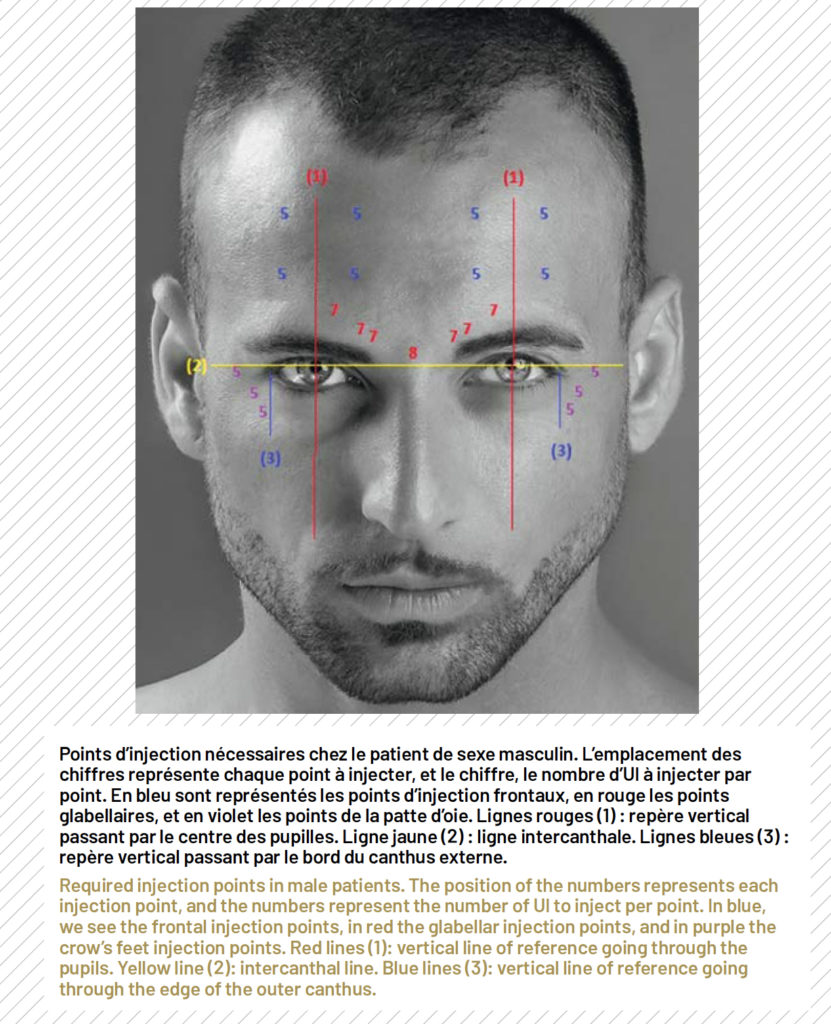
The greater mass of the procerus and corrugator muscles in men and the severity of their wrinkles lead to a lower response rate in men than in women. This greater muscle mass leads to a deep glabellar furrow, which gives a more aggressive appearance. In men, the corrugator muscle is thicker and requires deeper injection. Its lateral insertion is more stretched out, explaining why the traditional pattern of five injection points for the glabellar must often be completed with two additional, more external points. Treating the procerus muscle only requires one injection point, as in women. However, during the second session we must not hesitate to double the doses if the first session was ineffective due to the muscle’s strength, which is greater in men.
Forehead and eyebrows
Forehead lines usually need to be treated in conjunction with glabellar lines, as we must respect the position of the eyebrow which, in men, must remain horizontal in order to avoid feminising the face by arching it. Despite the precautions taken when treating the glabellar, as described above, the toxin ends up diff using and affecting the medial part of the frontalis muscle. It is important to treat these two areas in a harmonious way, as they are the two most expressive areas of a man’s face. The frontalis muscle, which is more powerful and wider in men than in women, requires more injection points (6 or even 8) as well as higher doses.
The more lateral points are important, to avoid lifting the tail of the eyebrow. They must sit along a vertical line that goes through the outer edge of the eye socket. What is more, it is important to keep in mind that we must not over-inject the frontalis muscle in men, to avoid losing the face’s expressiveness. If the eyebrow is already low and there is a risk of oedema or dermatochalasis in the upper eyelid, we would opt for the blanching technique using a suitable hyaluronic acid.
Crow’s feet
Crow’s feet wrinkles must be preserved to some extent when using botulinum toxin in men. They give the patient a more mature and distinguished appearance, which men generally wish to keep. They are more developed in men than in women, especially the lower wrinkles. It is important only to treat the central and lower wrinkles, and to leave the fine lines above as they give the face its masculine expression. The injection pattern is three points per side, using a single dose. They are placed in the lateral part of the orbicularis muscle, underneath the intercanthal line, in order to spare the fine lines above. Particular attention is paid to not placing the product too low or too high, or too deeply, so as not to affect the zygomatic muscles.
 Other indications
Other indications
In terms of aesthetics, there are other indications for using botulinum toxin in the face, which will not be addressed here. However we can mention the use of botulinum toxin in facial feminisation and particularly to treat hypertrophy in the master muscles, which allows us to slim down the face and soften the oval. Men are treated in a different way to women when we perform botulinum toxin injections for aesthetic purposes. This difference is due to their anatomy, on the one hand, as it diff ers between the sexes, and on the other hand it is because men’s expectations are often diff erent to women’s.
References
1. Bloom, J. D., Green, J. B., Bowe, W., von Grote, E. & Nogueira, A. Cosmetic Use of AbobotulinumtoxinA in Men: Considerations Regarding Anatomical Diff erences and Product Characteristics. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 15, 1056–1062 (2016).
2. Keaney, T. C. & Alster, T. S. Botulinum toxin in men: review of relevant anatomy and clinical trial data. Dermatol. Surg. Off . Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. Al 39, 1434–1443 (2013).
 Dr. Eloi de Clermont-Tonnerre: Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery. Masters in research from Harvard Medical School (Boston, USA).Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery and maxillofacial surgery department at the Henri-Mondor hospital in Créteil, run by Pr Meningaud.
Dr. Eloi de Clermont-Tonnerre: Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery. Masters in research from Harvard Medical School (Boston, USA).Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery and maxillofacial surgery department at the Henri-Mondor hospital in Créteil, run by Pr Meningaud.
 Pr Barbara Hersant: Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery.Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery and maxillofacial surgery department at the Henri-Mondor hospital in Créteil, run by Pr Meningaud.Scientific director of the AIME (Foundation for Innovation in Aesthetic Medicine and Surgery), general secretary of the French surgical academy, member of the SOFCPRE and the SOFCEP.
Pr Barbara Hersant: Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery.Plastic, reconstructive and aesthetic surgery and maxillofacial surgery department at the Henri-Mondor hospital in Créteil, run by Pr Meningaud.Scientific director of the AIME (Foundation for Innovation in Aesthetic Medicine and Surgery), general secretary of the French surgical academy, member of the SOFCPRE and the SOFCEP.
More informations: dr-hersant.fr